Course design
Concerning the course objectives, when it become obvious that producing software that helps DSD would affect future student projects, course content, and potentially also the ways how e-learning is used to deliver courses in virtually joined classrooms, a time-based model with two plains was created. The idea was to describe the way instructional and course design of the DSD course and results of student projects (especially in cases when student teams achieved greater progress) correlate.Instructional design phases (ADDIE model):
- Analysis
- Design
- Development
- Implementation
- Evaluation
- general requirements analysis, team forming
- concept presentation and acquirements of other teams' buy-in
- detailed design (*)
- development (**)
- QA testing
- release and maintenance (***)
(*) design is presented to other teams
(**) current project state is presented to other teams
(***) the results and product demo are presented to other teams
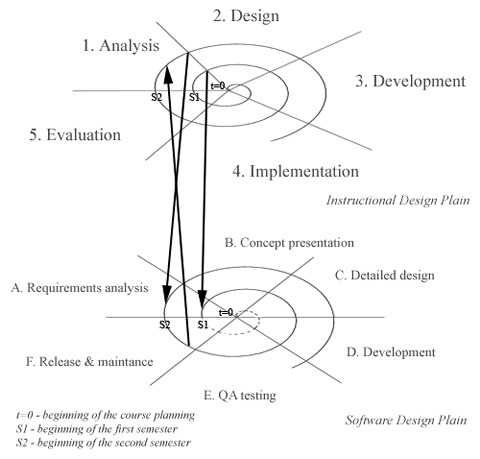
On the upper figure, on both plains, one cycle represents one delivery of the course, i.e. one semester. Initial instructional design was done a semester prior to the first delivery. One of the designers of the DSD course, a graduate student from Sweden, spent a semester in Zagreb during that period, planning and creating the course with his Croatian counterparts.
When the instructional design cycle reaches the “Analysis” phase, before considering changes for the next semester, the results of the students' software development projects are examined and evaluated in order to determine how they can make a meaningful contribution to the instructional and course design for the next semester. Later, during phases “A” and “B”, while deciding on future student projects during course delivery, instructional design cycle begins affecting software development cycle, setting priorities for future software development projects, team formations, inventive role-playing, etc.

